If you're interested in becoming a contributor or requesting changes then click here to join the discord
Difference between revisions of "OptogeniX"
Landonodnal (talk | contribs) (Created page with "Category:LinkedIn Accounts Category:Twitter Accounts Category:Organizations Category:Companies "OptogeniX origins from a research collaboration initiated in 20...") |
Landonodnal (talk | contribs) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Category:Companies]] | [[Category:Companies]] | ||
"OptogeniX origins from a research collaboration initiated in 2012 by neuroscientists from Harvard Medical School (HMS) and researchers from Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT). The aim of the collaboration was to develop new implantable probes for neurophysiology and optogenetics able to advance the limitations of the tools available at that time. The most important outcome of the research was a technology based on tapered fibers – and an unconventional way to launch light into them – that was soon recognized as unique and very useful for more versatile and efficient optogenetic stimulation of neurons in vivo." | "OptogeniX origins from a research collaboration initiated in 2012 by neuroscientists from Harvard Medical School (HMS) and researchers from Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT). The aim of the collaboration was to develop new implantable probes for neurophysiology and optogenetics able to advance the limitations of the tools available at that time. The most important outcome of the research was a technology based on tapered fibers – and an unconventional way to launch light into them – that was soon recognized as unique and very useful for more versatile and efficient optogenetic stimulation of neurons in vivo." | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:OptogeniX.png|thumb|OptogeniX Company Profile]] | ||
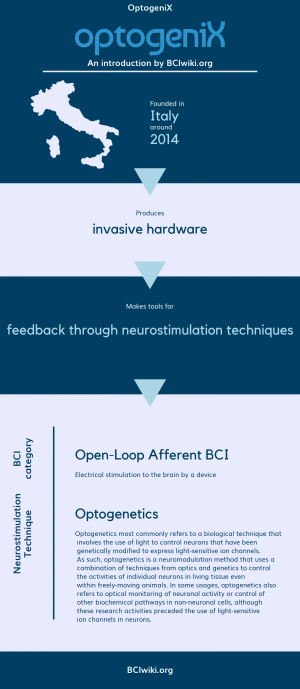
| + | Founded in Italy around 2014, OptogeniX produces invasive hardware. | ||
| + | |||
| + | OptogeniX makes tools for feedback through neurostimulation techniques. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Brain Computer Interface Classification|BCI Categories]]: Open-Loop Afferent | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[:Category:Neurostimulation_Techniques|Neurostimulation Technique(s)]]: Optogenetics | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Hardware== | ||
| + | *[[GalvoStation|GalvoStation]] | ||
| + | *[[Lambda_Fibers|Lambda Fibers]] | ||
| + | *[[ThetaStation|ThetaStation]] | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
[https://www.optogenix.com/ Website] | [https://www.optogenix.com/ Website] | ||
[https://www.linkedin.com/company/optogenix/ LinkedIn] | [https://www.linkedin.com/company/optogenix/ LinkedIn] | ||
[https://twitter.com/OptogeniX Twitter] | [https://twitter.com/OptogeniX Twitter] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:03, 17 February 2024
"OptogeniX origins from a research collaboration initiated in 2012 by neuroscientists from Harvard Medical School (HMS) and researchers from Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT). The aim of the collaboration was to develop new implantable probes for neurophysiology and optogenetics able to advance the limitations of the tools available at that time. The most important outcome of the research was a technology based on tapered fibers – and an unconventional way to launch light into them – that was soon recognized as unique and very useful for more versatile and efficient optogenetic stimulation of neurons in vivo."
Founded in Italy around 2014, OptogeniX produces invasive hardware.
OptogeniX makes tools for feedback through neurostimulation techniques.
BCI Categories: Open-Loop Afferent
Neurostimulation Technique(s): Optogenetics